How do you derive Heron’s Area Formula?
First of all, let us discuss what is Heron’s formula?
This formula is mainly used for finding the area of a triangle when all the length of all its sides is known. This is commonly referred to as Hero’s Formula and this formula can be used in finding out the areas of different types of triangles, like equilateral scalene, and isosceles triangles. By using this formula, one need not know the measurements of the angles of a triangle in order to calculate its area. This formula is not only used for calculating areas of triangles alone but also used for finding the area of the quadrilateral, which can be obtained by first dividing it into two trianglesalong its diagonal.
Considering a, b, and c to be the three sides of a triangle, then Heron’s formula can be written as:
Area of a triangle using the given three sides=√s(s−a)(s−b)(s−c)
Where s is the semi perimeter.
s = Perimeter of triangle/2 = (a+b+c)/2
A brief history of Heron’s Formula
The Hero of Alexandria was well known to be a great mathematician. He derived the formula which helps in calculating the area of a triangle by utilizing the length of the three sides of a triangle. With this, there is also an extension of the idea which helps in calculating the area of quadrilateral and also the areas of otherhigher-order polygons. This particular formula can be used for many applications like trigonometry which requiresproofof the law of cotangents and the law of cosines and many others.
Derivation of the Heron’s Formula
For a derivation of Heron’s formula, there are two methods. These are:
- The first one is by using the cosine rule and trigonometric identities.
- The second one is by solving algebraic expressions utilizingthe Pythagoras theorem.
In this article, we will discuss both methods of derivation.
- Using Cosine Rule
Let us consider a, b, c to be the sides and α, β, γ to bethe opposite angles to the sides of a given triangle.
We know that the law of cosines is
cos γ = (a2+b2+c2)/2ab
Using trigonometric identity, we have
Sinγ=√1−cos2γ
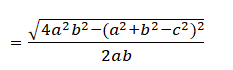
Let the base of the triangle = a and the height= b sinγ
Now, the area of a triangle = (base)(height)
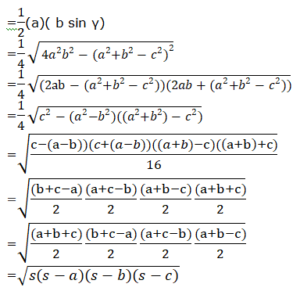
- By using Pythagoras theorem
Let us consider triangle ABC having sides a, b, and c as shown in the figure below:
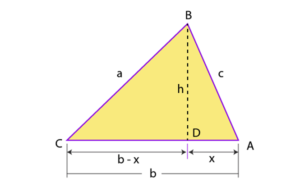
Area of a triangle =1/2 (base)(height)
Now the next step is to drop a perpendicular BD on AC as shown in the figure
Now, considering ∆ADB
From the figure, it is seen that by using Pythagoras theorem,
x2 + h2 = c2
x2 = c2 − h2
⇒x = √(c2−h2)
Now let us consider ∆CDB,
In this by using Pythagoras theorem
(b−x)2 + h2 = a2
(b−x)2 = a2 − h2
b2 − 2bx + x2 = a2–h2
By substituting the value of x and x2 from the above equations we get:
b2 – 2b√(c2−h2)+ c2−h2 = a2 − h2
b2 + c2 − a2 = 2b√(c2 − h2)
Squaring on both sides, we get;
(b2+c2–a2)2 = 4b2(c2−h2)
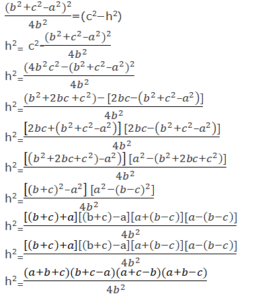
Now, the perimeter of an ∆ABC is
P= a+b+c
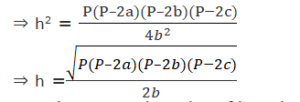
By substituting the value of h in the equation we get
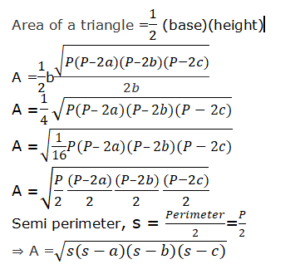
Application of Heron’s formula
Heron’s formula is a very popular formula for area calculation of various triangles and is applicable to calculate the area of quadrilateral and other polygons. The formula can be derived by two methods the law of cosines and the law of Cotangents.
How to solve the question below:
Q: If the area of an equilateral triangle is 16sqrt3 cm^(2), then the perimeter of the triangle is
- A) 48 cm
- B) 24 cm
- C) 12 cm
- D) 36 cm
Heron’s Formula for Quadrilateral
Let us see how to find the area of the quadrilateral by using Heron’s formula.
Consider a quadrilateral ABCD, in which AB||CD. Let AC be one of the diagonals which divide the quadrilateral ABCD into two triangles i.e.,∆ADC and ∆ABC.
Now we have two triangles here.
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of ∆ADC + Area of ∆ABC
Hence knowing the lengths of the sides of the quadrilateral ABCD and that of the diagonal AC, utilizing Heron’s formula one can find out the total area. By calculating the area of ∆ADC and that of ∆ABC using the Hero’s formula the area of the quadrilateral can be found out by adding them.